We use cookies to support this website, track usage on this website, to perform analytics and to perform promotional activities.
Click here to accept cookies.
TIC's Cookie Policy.
Privacy Policy
Frequency at 0% droop gain
Function
Droop control is a function that prevents loads from concentrating at a specific motor due to load imbalance when multiple inverters and motors are used to drive a common load.
These parameters are used to allow the motor to slip (drooping characteristic) according to the load torque current.
These parameters are used to adjust the frequency range, deadband torque, and gain.
Setting methods
• Droop control is enabled when [Pt: V/f Pattern] is set to "3", "9", "10", or "11".
• When the applied torque is equal to or more than the deadband torque value, output frequency is reduced during power running or increased during regeneration.
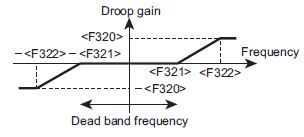
• Droop control is enabled at frequency range [F321: Frequency at 0% droop gain] or more.
• The amount of droop will vary depending on the output frequency for frequency ranges [F321: Frequency at 0% droop gain] or more or [F322: Frequency at F320 droop gain] or less.
• For the frequency range over [vL: Base frequency 1], the amount of error for [F323: Droop deadband torque] will increase. Therefore, we recommend you use this parameter at base frequency or less.
• Output frequency in droop control will not be limited by [FH: Maximum frequency].
Calculating formula
The amount of output frequency adjusted by droop control can be calculated with the following formula.
Gain based on internal torque command (Gain 1)
• When internal torque command (%) ]= 0, Gain 1 = (internal torque command - [F323])/100
Note that 0 (zero) or a positive number must be set to Gain 1.
• When internal torque command (%) [ 0, Gain 1 = (internal torque command + [F323])/100
Note that 0 (zero) or a negative number must be set to Gain 1.
Gain based on frequency after acceleration (Gain 2)
• When [F321] [ [F322]
When |frequency after acceleration| [= [F321], Gain 2 = 0
When |frequency after acceleration| ] [F322], Gain 2 = [F320]/100
When [F321] [ |frequency after acceleration| [= [F322], Gain 2 = ([F320]/100) x ((|frequency after acceleration| - [F321])/([F322] - [F321]))
• When [F321] ]= [F322]
When |frequency after acceleration| [= [F321], Gain 2 = 0
When |frequency after acceleration| ] [F321], Gain 2 = [F320]/100
Droop frequency
Droop frequency = [vL: Base frequency 1] x Gain 1 x Gain 2
Note that, when [vL: Base frequency 1] is over 100 Hz, this value is calculated as 100 Hz.
Please reference latest AS3 Instruction Manual more details or latest information.
AS3 fault codes, descriptions, symptoms and suggested remedies can be found in the below links. Each fault code can also be linked to directly from the AS3 by accessing the QR code on a mobile device while the AS3 is currently experiencing the fault.

Welcome to Toshiba International Corporation's Download Site!
Register to view our materials and keep informed with our latest updates.
You may enter your filters below to locate manuals, brochures, software, drawings, and other important documents.
Select a category, choose a Product Family, then select from the list of available documents.
If you encounter any problems or have any questions please contact TIC-Webmaster@toshiba.com
- Tools & Resources
- Resource Library
- Literature & Promotional Request
- Training
- FAQs
- Image Gallery
- Mobile Apps
- Videos
- Service & Warranty
- Where to Buy & Service
- TOSHcare®
- Service Request Forms
- General Warranty & Product Registration
- Motor Warranty Claims Procedure
- Support Contacts
Sign me up to receive future updates about Toshiba products
Yes NoI have read and agree to the Privacy Policy



